What Is Web3.0? Future of the Internet.
- Tech Innovation
Admin
- July 10, 2019
- 0

‘What is web3’ – Future of the internet : Since the Internet was invented in the 1990s, it has continued to grow rapidly while changing the world as we know it. It all started with Web 1.0 which people also call “read-only web” or “static web” with web pages with static content mostly in text or image format. Some people describe it as “a one-way street with a narrow aisle, where content creation is done by a select few and information mostly comes from directories”, making it extremely difficult for users to use. in finding relevant information.
The next step is Web 2.0, or “social web”, which is more interactive thanks to advances in web technologies like Javascript, HTML5, CSS3, etc. and introduce new platforms like Youtube, Facebook, MySpace, Wikipedia, etc. Web2 refers to the version of the Internet that most of us are familiar with today. The rise of Web 2.0 was largely driven by three main layers of innovation: mobile, social, and cloud. The internet is dominated by large companies that offer services in exchange for your personal data. However, people are slowly waking up and realizing how important this personal data is when it is in the hands of these big companies.
So that brings us to the next stage of the Internet, Web 3.0. What is Web 3.0 and what changes will it bring to the Internet as we know it today? Many say that 3.0 combines the decentralized, community-driven features of Web1 with the cutting-edge, modern features of Web2. While improving Web2, Web3 also has many other features that will help transform the Internet, such as:
- Verifiable
- Trustless
- Self-governing
- Permissionless
- Distributed and robust
- Stateful
- Native built-in payments’

Summary : Web3 is considered the future of the Internet. The vision for this new blockchain-based website includes cryptocurrency, NFT, DAO, decentralized finance and more. It provides a read/write/clean version of the web where users have a financial stake and more control over the web community they belong to. Web3 promises to change the online experience completely just like PCs and smartphones have done. However, it is not without risks. Several companies have entered the field only to face backlash over the environmental impact and financial speculation (and potential fraud) that accompanies Web3 projects. And while blockchain is being touted as a solution to the problems of privacy, centralization, and financial exclusion, it has created new versions of many of these problems. Businesses need to weigh both the risks and the benefits before starting.
How does Web 3 work?
With Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 technologies, HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) defines the layout and delivery of web pages. HTML will continue to be the base layer with Web 3.0, but the way it connects to data sources and where those data sources reside may be slightly different from previous web generations.
Many websites and almost all applications in the Web 2.0 age rely on some form of centralized database to provide data and help enable functionality. With Web 3.0, instead of a centralized database, applications and services use a decentralized blockchain. With blockchain, the basic idea is that there is no arbitrary central authority, but a form of distributed consensus. An emerging governance ideal in the blockchain and Web 3.0 communities is the concept of a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO). Instead of having a central authority managing a platform’s operations, with DAOs, Web 3.0 communities and technologies provide a form of self-governance that seeks to follow a decentralized approach.
Basically, Web 3.0 also works with cryptocurrencies, more than fiat. Finance and the ability to pay for goods and services with a decentralized payment method enabled on Web 3.0 through the use of cryptocurrencies, all built and powered on top of blockchain technology.
Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 were primarily built with the IPv4 address space in mind. Due to the strong growth of the Web over the decades, Web 3.0 needs more Internet addresses than IPv6 provides.
Key Web 3 features
Web 3.0 can be built with artificial intelligence, the Semantic Web, and common attributes. The idea behind using AI comes from the goal of providing faster and more relevant data to the end user. A website using AI should be able to filter and provide data that it thinks a particular user would find relevant. Social bookmarking as a search engine can provide better results than Google because the results are sites that users have voted for. However, these results can also be manipulated by humans. AI can be used to separate legitimate results from bogus ones, producing results similar to social bookmarking and social media, but without the bad feedback.
An artificially intelligent web will also introduce virtual assistants, something that has emerged today as an aspect in devices or through third-party applications.

The idea behind the Semantic Web is to classify and store information in a way that helps teach the system the meaning of particular data. In other words, a website must be able to understand words placed in search queries in a human-like manner, which allows it to create and share better content. The system will also use AI; The semantic web will teach the computer what the data means, and then the AI will take the information and use it. There are several key features of Web 3.0 that help define what the third generation of the web is likely to become, including the following:
Decentralized. Unlike the first two Web generations, where administration and applications were largely centralized, Web 3.0 will be decentralized. Applications and services will be enabled in a distributed approach where there is no central authority. Based on blockchain. Blockchain is the catalyst for creating decentralized applications and services. With blockchain, data and connections between services are distributed in a different approach to centralized database infrastructure. Blockchain can also enable an immutable record of transactions and activities, helping to provide verifiable authenticity in a decentralized world. Compatible with cryptocurrencies. The use of cryptocurrencies is a key feature of Web 3.0 services and has largely replaced the use of fiat currency. Autonomy and artificial intelligence. More automation overall is a core feature of Web 3.0, and much of that automation will be powered by AI.
Web 3.0 applications
With blockchain at its core, Web 3 enables a growing variety of new applications and services to exist, including:
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.NFT. Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) are tokens that are stored in a blockchain with a cryptographic hash, making the token unit unique.
- DeFi. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging use case for Web 3.0 where decentralized blockchain is used as the basis for enabling financial services, outside of the confines of a traditional centralized banking infrastructure.
- Cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are Web 3.0 applications that create a new world of currency that aims to be separate from the historical world of fiat currency.
- dApp. Decentralized applications (dApps) are applications that are built on top of blockchain and make use of smart contracts to enable service delivery in a programmatic approach that is logged in an immutable ledger.
- Cross-chain bridges. There are multiple blockchains in the Web 3.0 world, and enabling a degree of interoperability across them is the domain of cross-chain bridges.
- DAOs. DAOs are set to potentially become the organizing entities for Web 3.0 services, providing some structure and governance in a decentralized approach.
Web 3.0 vs. Web 2.0
Web 3.0 is the successor of the previous two generations of the Web.
The first generation of the Web, sometimes called Web 1.0, was invented and defined by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989. Web 1.0 was about basic access and connectivity between static web pages. The first generation of the web lasted until about 2004, when Tim O`Reilly helped coin the term Web 2.0.
Web 2.0 refers to websites and applications that use user-generated content for end users. Web 2.0 is used in many websites today, focusing primarily on user interaction and collaboration. Web 2.0 also aims to provide more universal networking and communication channels.
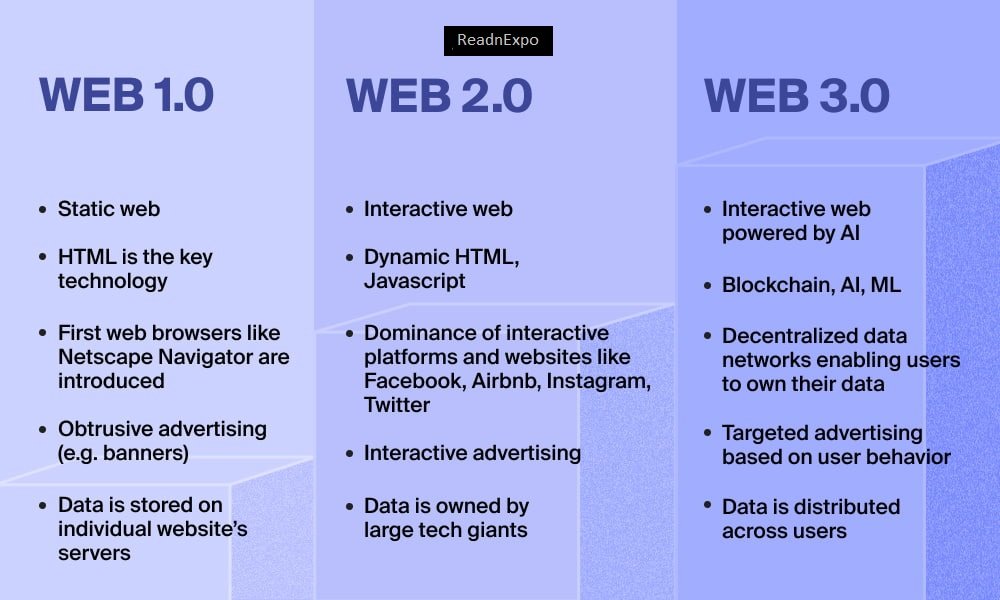
The difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 is that Web 3.0 is more focused on using technologies like machine learning and AI to deliver tailored content to each user rather than content provided by end users. . Essentially, Web 2.0 allows users to contribute and sometimes collaborate on web content, while Web 3.0 will most likely leave those tasks to the Semantic Web and AI technologies. Web 3.0 also has a strong focus on decentralized services and authority, which is in sharp contrast to the centralization of Web 2.0.




